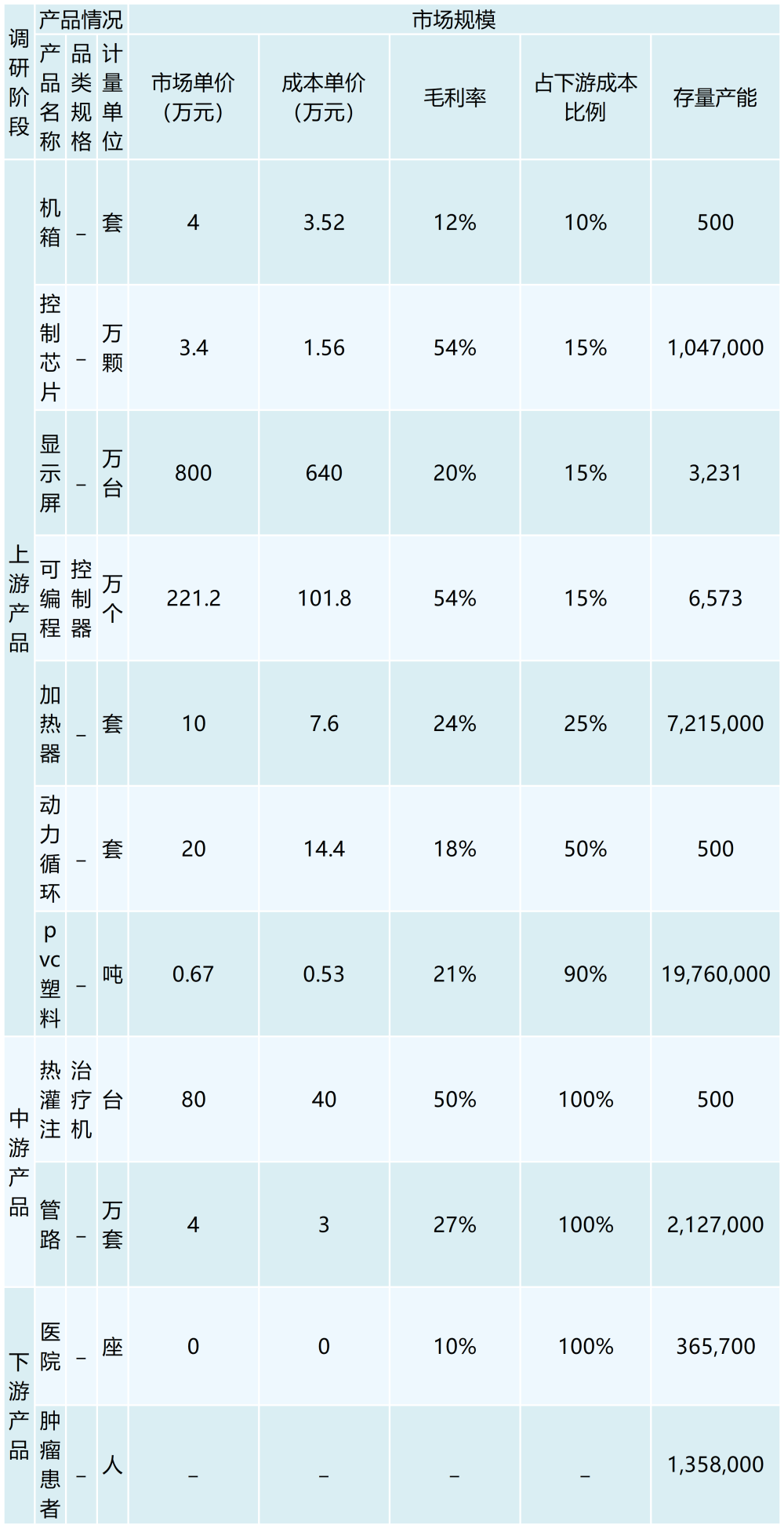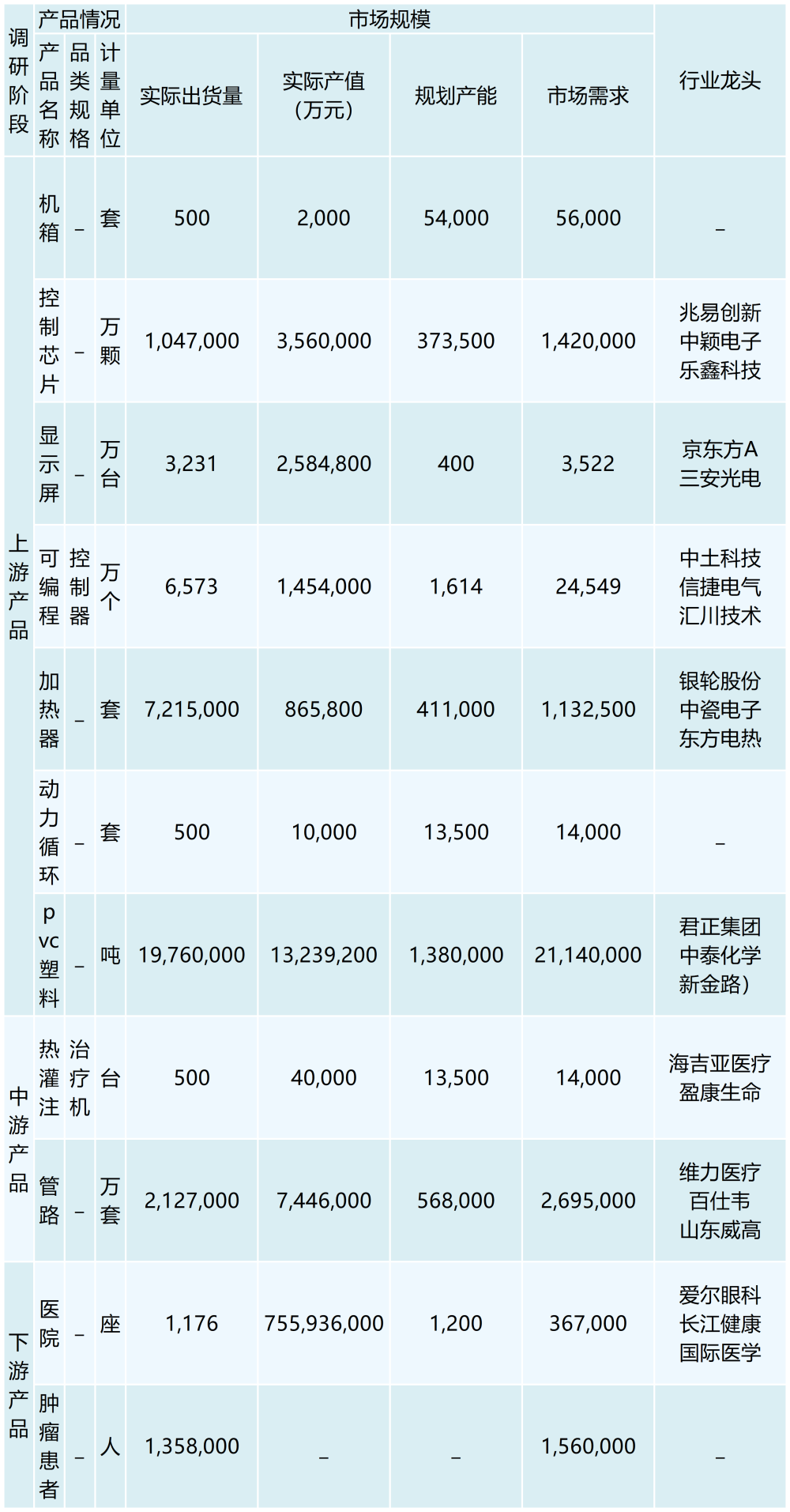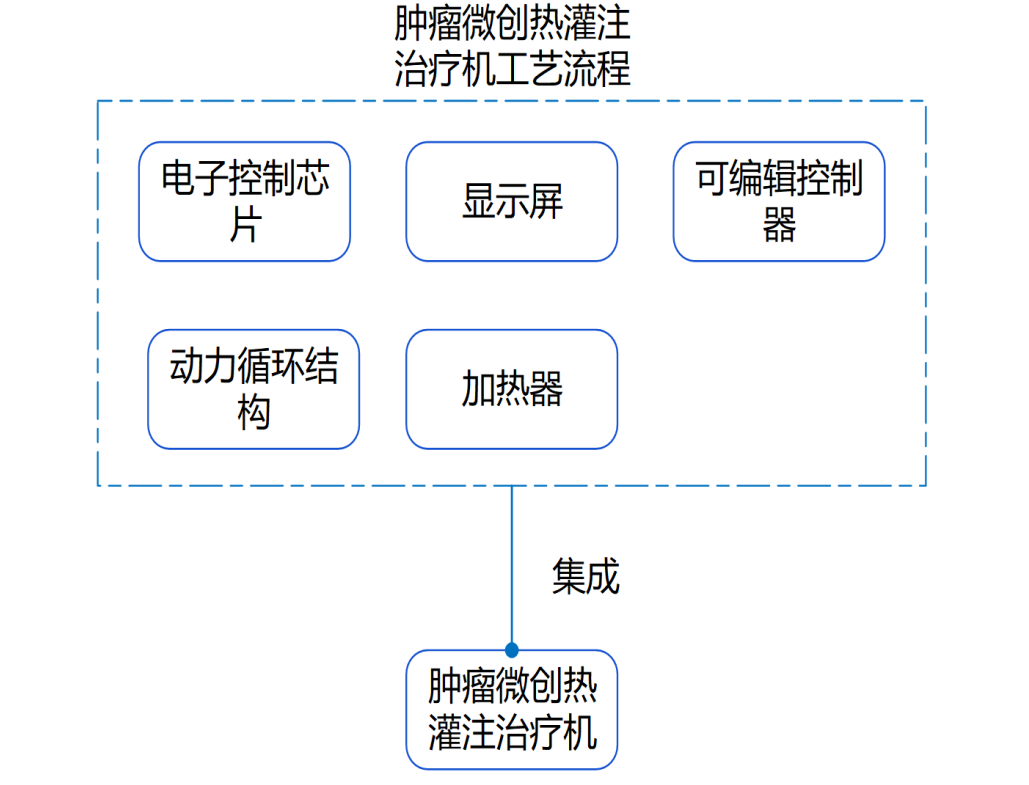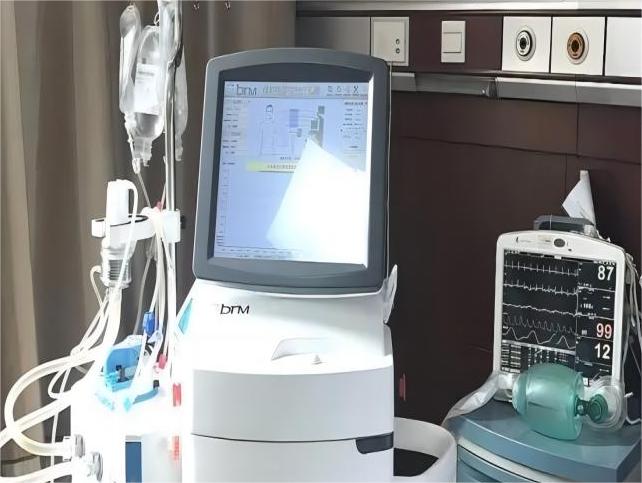
Gastric, intestinal and esophageal cancers are common malignant tumors of the digestive system in China. In 2021, the number of people suffering from malignant tumors of the digestive system in China will increase by 1,358,000 people, accounting for one-third of the number of people suffering from new cancers in China in 2021. Tumor pathogenesis is that the genes in the human body under the action of carcinogenic factors, the genes have mutated, lost the normal regulation of the cells themselves, so that their unrestricted growth, and later can be transferred to other parts of the body, producing harmful substances, the body organs and tissues caused by the destruction of the body, a serious danger to the body's health. Thermal perfusion chemotherapy is a newly developed tumor treatment technology in recent years, which can effectively treat malignant tumors of local stomach, intestines, esophagus and other digestive systems. The main treatment mechanism of thermal perfusion therapy is that the tumor treatment drugs are heated up to more than 43℃ through the thermal perfusion therapy machine, which can make the tumor cells die without affecting the normal tissues at the same time, and through the catheter to make the human body connected to the thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity with the thermal perfusion therapy instrument. Through the catheter, the thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity of the human body are connected with the thermal perfusion therapy instrument, so that the therapeutic drugs can form a cycle between the human body and the thermal perfusion therapy instrument to maintain the therapeutic temperature and effectively kill the tumor cells; at the same time, the cancer cells can be effectively eliminated from the body through the role of mechanical scrubbing, and at present, there are more than 500 hospitals in our country have begun to apply the thermal perfusion therapy machine, and the market scale has reached 400 million yuan, and the market size is expected to be up to tens of billion dollars.