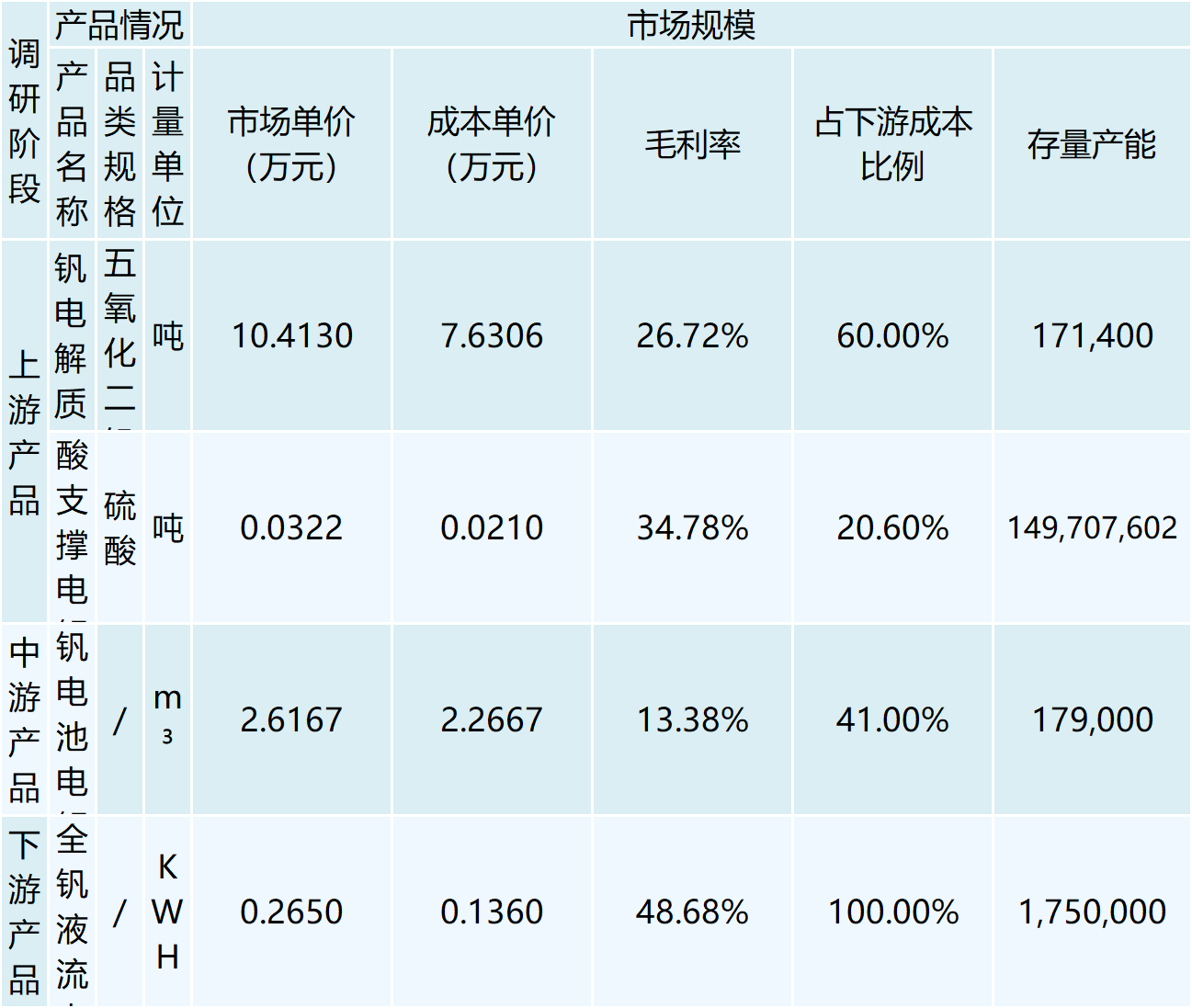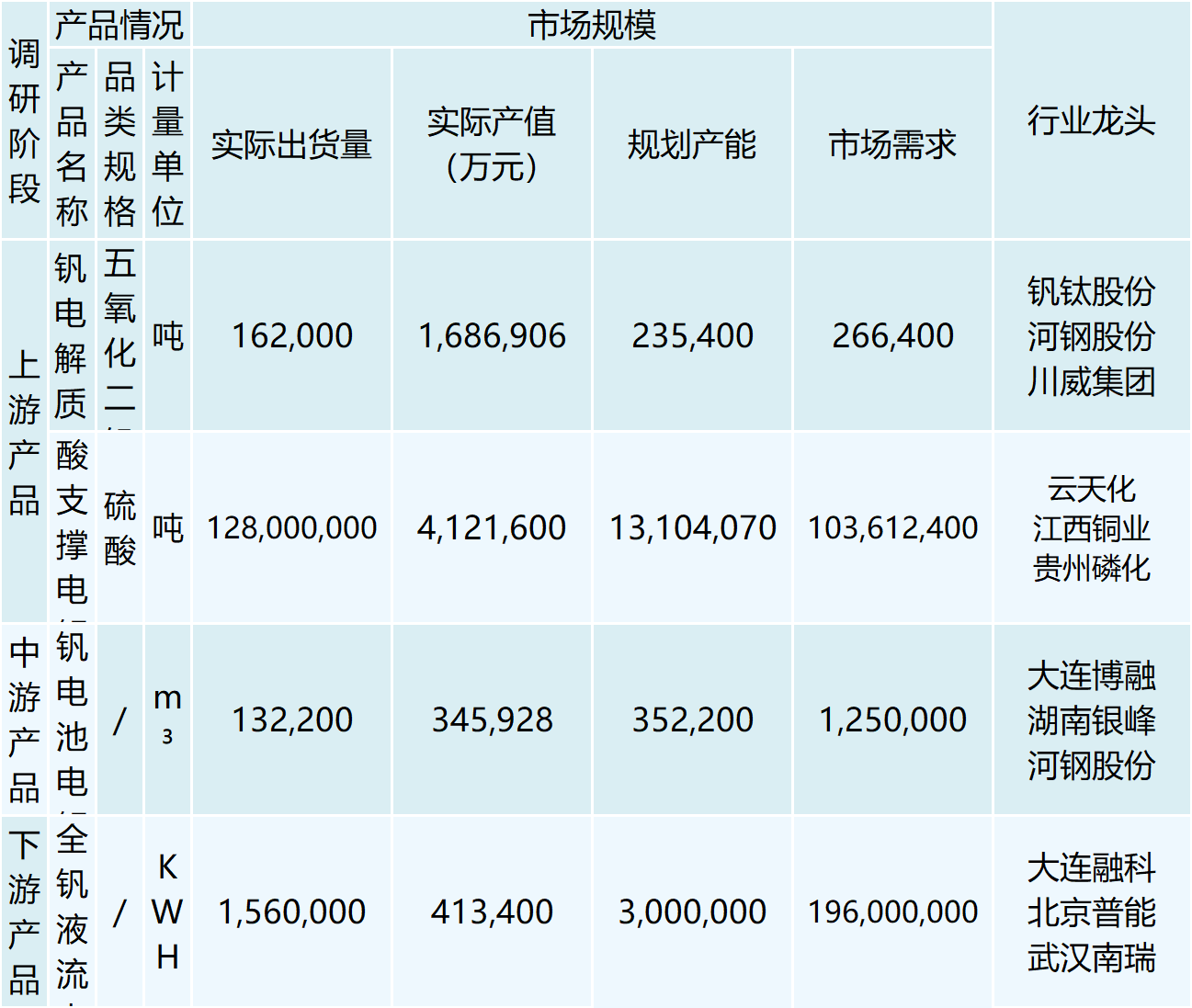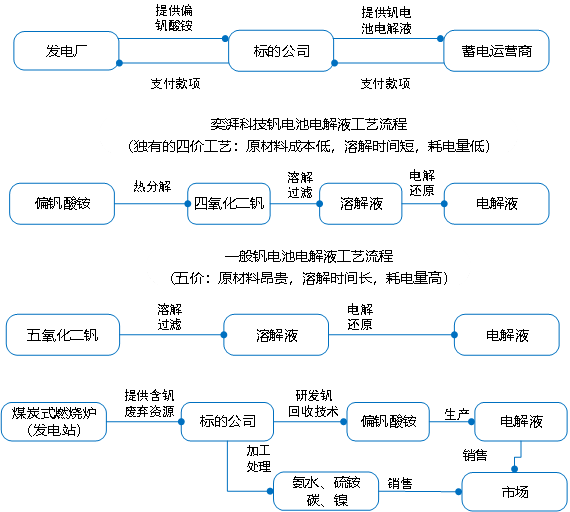
The vanadium battery electrolyte is the key material in an all-vanadium liquid flow battery (VRB), and it directly acts as the positive and negative electrodes of the battery system. The positive electrolyte of a vanadium battery is a sulfuric acid solution containing tetravalent and pentavalent vanadium ions, and the negative electrolyte is a sulfuric acid solution containing divalent and trivalent vanadium ions. The positive and negative electrolyte undergoes redox reaction on both sides of the ion exchange membrane, and the electrolyte is pressed into the battery stack by an external pump, which is mechanically powered to circulate in a closed loop of different tanks and half-cells, thus realizing the storage and release of electrical energy. Electrolysis is currently the most widely used preparation method, possessing good electrochemical activity and reversibility, simpler, less likely to introduce new impurities, and lower preparation costs. According to the report of LDJH, it is expected that by 2025, the demand for vanadium pentoxide pulled by vanadium batteries will reach 61-129,000 tons, and if the price of vanadium pentoxide is stabilized at 100,000 yuan/ton, the corresponding market size will reach 6.1 billion yuan and 12.9 billion yuan, respectively. According to the report forecast by XYZ-Research, China's all-vanadium liquid current battery market size will be expected to reach more than 8 billion yuan by 2025, with an average growth rate of about 188.9% during the period of 2022-2025.